| A P P E N D I X B |
|
Mount Options in a Sun StorageTek QFS Shared File System |
The Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system can be mounted with several mount options. This appendix describes some of these options within the context of their roles.
You can specify most mount options by using the mount(1M) command, by entering them in the /etc/vfstab file, or by entering them in the samfs.cmd file. For example, the following /etc/vfstab file includes mount(1M) options for a Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system:
You can change some mount options dynamically by using the samu(1M) operator utility. For more information about these options, see Using the samu(1M) Operator Utility.
The following sections summarize the mount options available to you in a Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system. For more information about any of these mount options, see the mount_samfs(1M) man page or see the cross-references mentioned in their descriptions.
The bg mount option specifies that if the first mount operation fails, subsequent attempts at mounting should occur in the background. By default, bg is not in effect, and mount attempts continue in the foreground.

|
Caution - Do not use this option if you are mounting a Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system on a Sun Cluster node or if you have shared Sun StorageTek QFS clients outside the cluster. |
The retry mount option specifies the number of times that the system should attempt to mount a file system. The default is 10000.
The shared mount option declares a file system to be a Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system. This option must be specified in the /etc/vfstab file in order for the file system to be mounted as a Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system. The presence of this option in a samfs.cmd file or on the mount(1M) command does not cause an error condition, but it does not mount the file system as a Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system.
The -o minallocsz=n and -o maxallocsz=n options to the mount(1M) command specify an amount of space, in kilobytes. This is the minimum block allocation size. If a file is growing, the metadata server allocates blocks when an append lease is granted. You can use the -o minallocsz=n option to specify the initial size of this allocation. The metadata server can increase the size of the block allocation depending on the application's access patterns up to, but not exceeding, the -o maxallocsz=n option's setting.
You can specify these mount(1M) options on the mount(1M) command line, in the /etc/vfstab file, or in the samfs.cmd file.
A lease grants a shared host permission to perform an operation on a file for as long as the lease is valid. The metadata server issues leases to each shared host, including itself. The leases are renewed as necessary to permit continued file operations. The possible file operations are as follows:
A shared host can continue to update leases for as long as necessary. The lease is transparent to the end user. TABLE B-1 shows the mount options that enable you to specify the duration of each lease type.
All three leases enable you to specify an n such that 15 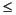 n
n 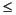 600. The default time for each lease is 30 seconds. A file cannot be truncated if a lease is in effect. For more information about setting these leases, see the mount_samfs(1M) man page.
600. The default time for each lease is 30 seconds. A file cannot be truncated if a lease is in effect. For more information about setting these leases, see the mount_samfs(1M) man page.
If you change the metadata server because the current metadata server is down, you must add the lease time to the changeover time because all leases must expire before an alternate metadata server can assume control.
Setting a short lease time causes more traffic between the client hosts and the metadata server because the lease must be renewed after it has expired. For information on lease times in a Sun Cluster environment, see the Sun StorageTek QFS Installation and Upgrade Guide.
By default, in a Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system, multiple hosts can read the same file at the same time, and if no host is writing to that file, I/O can be paged on all hosts. Only one host can append or write to a file at any one time.
The mh_write option controls write access to the same file from multiple hosts. If mh_write is specified as a mount option on the metadata server host, the Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system enables simultaneous reads and writes to the same file from multiple hosts. If mh_write is not specified on the metadata server host, only one host can write to a file at any one time.
By default, mh_write is disabled, and only one host has write access to a file at any one time. The length of that time period is determined by the duration of the wrlease mount option. If the Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system is mounted on the metadata server with the mh_write option enabled, simultaneous reads and writes to the same file can occur from multiple hosts.
TABLE B-2 describes how file access from multiple hosts is affected depending on whether the mh_write option is enabled on the metadata server.
|
Only one append host is allowed. |
The mh_write option does not change locking behavior. File locks behave the same whether mh_write is in effect or not. The mh_write option's effect is as follows:
Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system maintains consistency between hosts. The first time that a host executes a read or write system call, it gets a lease, which enables it to read or write the file for some period of time. The existence of that lease prevents other hosts without mh_write from accessing the file. In particular, the lease can last longer than the duration of the system call that caused its acquisition.
When mh_write is not in effect, the Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system should provide near-POSIX behavior for data reads and writes. For metadata, however, access time changes might not be seen immediately on other hosts. Changes to a file are pushed to disk at the end of a write lease, and when a read lease is acquired, the system invalidates any stale cache pages so that the newly written data can be seen.
When mh_write is in effect, behavior might be less consistent. When there are simultaneous readers and writers, the Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system switches all hosts accessing the file into direct I/O mode. This means that page-aligned I/O should be visible immediately to other hosts. However, non-page-aligned I/O can result in stale data being visible, or even written to the file, because the normal lease mechanism that prevents this has been disabled.
You should specify the mh_write option only when multiple hosts need to write to the same file simultaneously and when applications perform page-aligned I/O. In other cases, there is some risk of data inconsistency because even using flock() (which works with mh_write) to coordinate between hosts does not guarantee consistency.
For more information about mh_write, see the mount_samfs(1M) man page.
The min_pool=n mount option sets the minimum number of concurrent threads for the Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system. By default, min_pool=64 on Solaris systems, or 8 on Linux clients. This means that using default settings, there will always be at least 64 active threads in the thread pool on Solaris and 8 on Linux. You can adjust the min_pool=n mount option to any value between 8 and 2048, depending on the Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system's activity.
The min_pool mount option must be set in the samfs.cmd file. It will be ignored if set in the /etc/vfstab file or on the command line.
The meta_timeo=n mount option determines how long the system waits between checks on the metadata information. By default, the system refreshes metadata information every three seconds. This means, for example, that an ls(1) command entered in a Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system with several newly created files might not return information about all the files until three seconds have passed. For n, specify a value such that 0 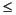 n
n 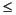 60.
60.
By default, data files in the Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system are allocated using the round-robin file allocation method. To specify that file data be striped across disks, you can specify the stripe mount option on the metadata host and all potential metadata hosts. Note that by default, unshared file systems allocate file data using the striped method.
In a round-robin allocation, files are created in a round-robin fashion on each slice or striped group. This causes the maximum performance for one file to be the speed of a slice or striped group. For more information about file allocation methods, see Design Basics.
You can set the sync_meta=n option to sync_meta=1 or sync_meta=0.
By default, sync_meta=1 and a Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system writes file metadata to disk every time the metadata changes. This slows data performance, but it ensures data consistency. This is the setting that must be in effect if you want to change the metadata server.
If you set sync_meta=0, the Sun StorageTek QFS shared file system writes the metadata to a buffer before writing it to disk. This delayed write delivers higher performance, but it decreases data consistency after an unscheduled machine interruption.
If you are using the optional WORM package, the worm_capable mount option enables the file system to support WORM files. The def_retention mount option sets the default retention time using the format def_retention=MyNdOhPm.
In this format, M, N, O, and P are non-negative integers and y, d, h, and m stand for years, days, hours, and minutes, respectively. Any combination of these units can be used. For example, 1y5d4h3m indicates 1 year, 5 days, 4 hours, and 3 minutes; 30d8h indicates 30 days and 8 hours; and 300m indicates 300 minutes. This format is backward compatible with the formula in previous software versions, in which the retention period was specified in minutes.
See Configuring WORM-FS File Systems for more information about the WORM functionality.
Copyright © 2007, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.