

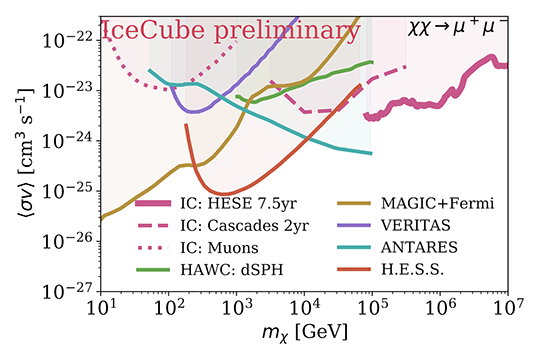
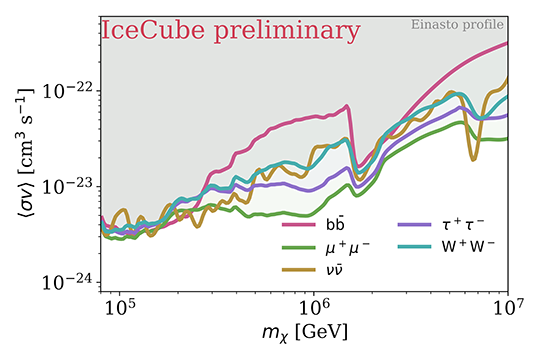
Comparison of the dark matter velocity averaged self-annihilation cross-section limits for a benchmark channel (χχ->μμ) between different experiments; previous IceCube MESE analysis [20], previous IceCube muon analysis [26], HAWC dwarf spheroidal analysis [27], MAGIC and FermiLAT combined analysis [28], VERITAS [5], ANTARES [29] and H.E.S.S. [30]. An Einasto halo profile following [19] is assumed.
Comparison of the dark matter velocity averaged self-annihilation cross-section limits for a benchmark channel (χχ->μμ) between different experiments; previous IceCube MESE analysis [6], previous IceCube muon analysis [7], HAWC dwarf spheroidal analysis [8], MAGIC and FermiLAT combined analysis [9], VERITAS [5], ANTARES [10] and H.E.S.S. [11]. An Einasto halo profile following [0] is assumed.2
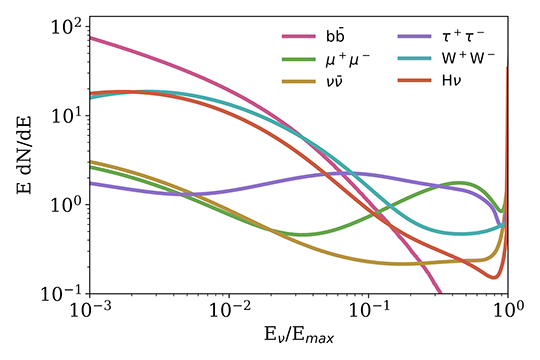
Simulated neutrino spectra in the dark matter rest-frame for all investigated annihilation/decay channels. Emax denotes the dark matter mass/half the dark matter mass for annihilation/decay respectively. At the high masses considered here, the shape of the spectra is, up to a scaling factor, identical for all masses.
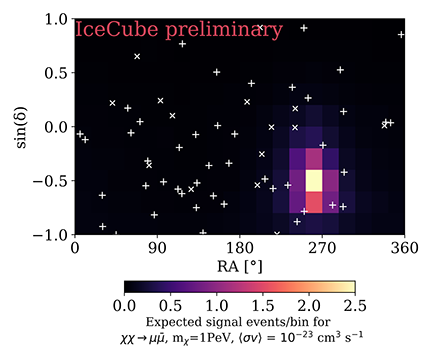
The colour map shows the expected neutrino signal events in each analysis bin for a dark matter annihilation model with: χχ->μμ, m=1PeV, <σv>=10^-23 cm^3/s. The white '+' and 'x' marks show the best fit directions of HESE (double) cascade and track events respectively. HESE events below 60TeV are not shown as they are not considered in this analysis. An Einasto halo profile following [19] is assumed.
<
4 - 4
>