Definition of the prompt component
Prompt muon: parent is not pion or kaon
Conventional muon: parent is pion or kaon
A comparison between CORSIKA standalone and MCEq is shown in Fig. 16.
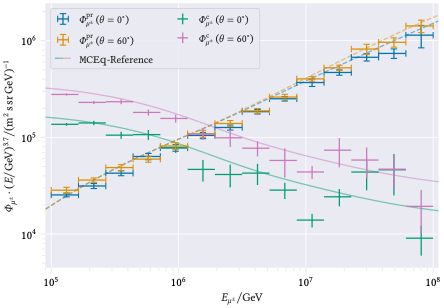
Fig. 16 : Comparison of the muon flux between CORSIKA standalone and MCEq.
A comparison between CORSIKA in icetray step 0 and MCEq is shown in Fig. 17. In that plot, the CORSIKA simulation was performed for zenith angles from 0 to 90 degrees.
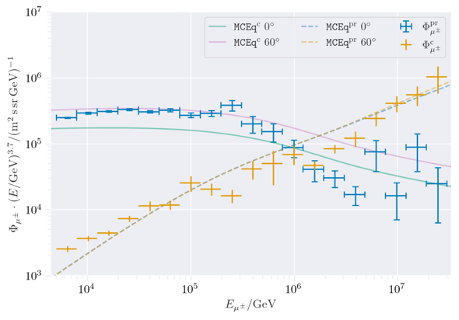
Fig. 17 : Comparison of the muon flux between CORSIKA simulated in icetray at step 0 and MCEq.
In this comparison it is important to note that neither MCEq nor CORSIKA are correct. CORSIKA is full Monte Carlo simulation tool to simulate the air shower, while MCEq is a tool to solve the cascade equations numerically. Hence, both tools use two different approaches to solve the same problem, but a mismatch between the two does not indicate which method is correct.
All in all, both methods lead to similar results considering the statistical uncertainties. Some deviations could be explained by the different versions of the hadronic interaction model SIBYLL. In CORSIKA, version 2.3d is used, in MCEq version 2.3c is used.
This work is based on the Master thesis of Ludwig Neste, which can be downloaded here. Other definitions of the prompt component are possible as well and can be found in Ludwig’s thesis.
These investigations and even further studies are uploaded to the arxiv and available here. The manuscript has been successfully published in EPJ C and can be found here.